
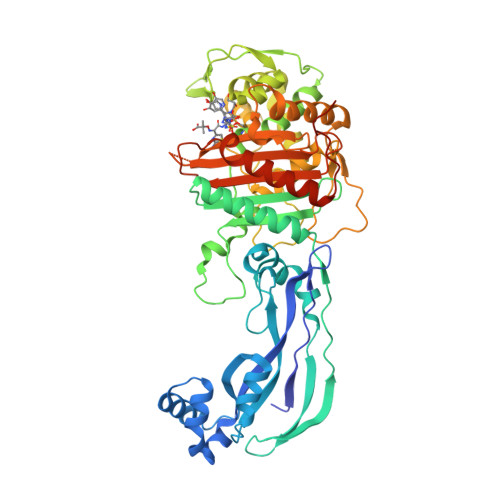
However, this strain expressing only the essential PBPs showed deficiencies in virulence and antibiotic resistance ( 10). aureus are the monofunctional high-molecular-weight transpeptidase, PBP1, and the bifunctional PBP2 (glycopolymerase/transpeptidase) ( 10). It has been previously demonstrated that the only essential penicillin-binding proteins (PBPs) in S. Although broad-spectrum MRSA resistance to β-lactam antibiotics has long been attributed to impaired acylation of the mecA gene product, penicillin-binding protein 2a (PBP2a) ( 2), recent evidence shows penicillin-binding protein 4 (PBP4), a low-molecular-weight monofunctional transpeptidase, can facilitate antibiotic resistance independently of PBP2a ( 3, – 9). Resistance to β-lactam antibiotics seen in MRSA is especially serious as they remain the most widely prescribed class globally, typically having a favorable safety profile and being relatively affordable and accessible. Indeed, the 2017 World Health Organization report, Priority Pathogens List for R&D of New Antibiotics, listed MRSA as a “high” priority pathogen for the development of new antimicrobials ( 1).
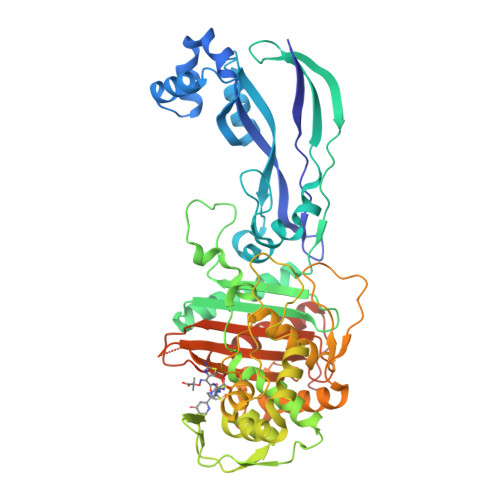
Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) 3 infections are a serious cause of both nosocomial and community-acquired infections, causing mortality and morbidity throughout the world. aureus CRB has at least two PBP4-mediated resistance mechanisms. However, ceftaroline resistance appeared to be mediated by other factors, possibly including mutation of the pbp4 promoter. With ceftobiprole, the missense mutations impaired the K m value 150-fold, decreasing the proportion of inhibited PBP4. Localized within the transpeptidase active-site cleft, the two substitutions appear to have different effects depending on the drug. In parallel, we characterized the structural and kinetic effects of the PBP4 mutations present in the CRB strain. We present the first crystallographic PBP4 structures of apo and acyl-enzyme intermediate forms complexed with three late-generation β-lactam antibiotics: ceftobiprole, ceftaroline, and nafcillin. To better understand PBP4's role in resistance, here we have characterized its kinetics and structure with clinically relevant β-lactam antibiotics. This strain has two missense mutations in pbp4 and a mutation in the pbp4 promoter, both of which play an instrumental role in β-lactam resistance.
PBP3 PDB SERIAL
Previously, we have shown that broad-spectrum β-lactam resistance can arise following serial passaging of a mecA-negative COL strain of S. Although β-lactam resistance in MRSA has been ascribed to the acquisition and activity of penicillin-binding protein 2a (PBP2a, encoded by mecA), it has recently been observed that resistance can also be mediated by penicillin-binding protein 4 (PBP4).

MRSA strains are resistant to a variety of antibiotics, including the classic penicillin and cephalosporin classes of β-lactams, making them intractable to treatment.

Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) causes serious community-acquired and nosocomial infections worldwide.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
